Power stations, also known as power plants or generating stations, are at the heart of modern civilization. These facilities convert various forms of energy into electrical power, which fuels homes, industries, transportation systems, and virtually every aspect of daily life. Whether we realize it or not, nearly everything we do — from switching on a light to charging a phone — depends on the uninterrupted operation of power stations.
However, when venturing outdoors or camping, access to these traditional power sources isn’t always possible. This is where Camping Power Banks: Staying Charged in the Great Outdoors become invaluable. These portable devices allow adventurers to keep their phones, GPS units, and other essential electronics powered, ensuring safety, connectivity, and convenience even in the most remote locations.
What is a Power Station?
It typically includes a generator, turbines, fuel source, and infrastructure for transmitting power to the grid. Depending on the energy source used, power station are classified into different types: thermal, hydroelectric, nuclear, solar, and wind, among others.
Types of Power Stations
There are several main types of power stations, each utilizing different energy sources and technologies.
1. Thermal Power Stations
These are the most common types and rely on fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, or oil.
- Coal-fired plants are the traditional backbone of many power grids but are increasingly being phased out due to their environmental impact.
- Gas-fired plants are cleaner and more efficient, often used for backup or peak demand electricity.
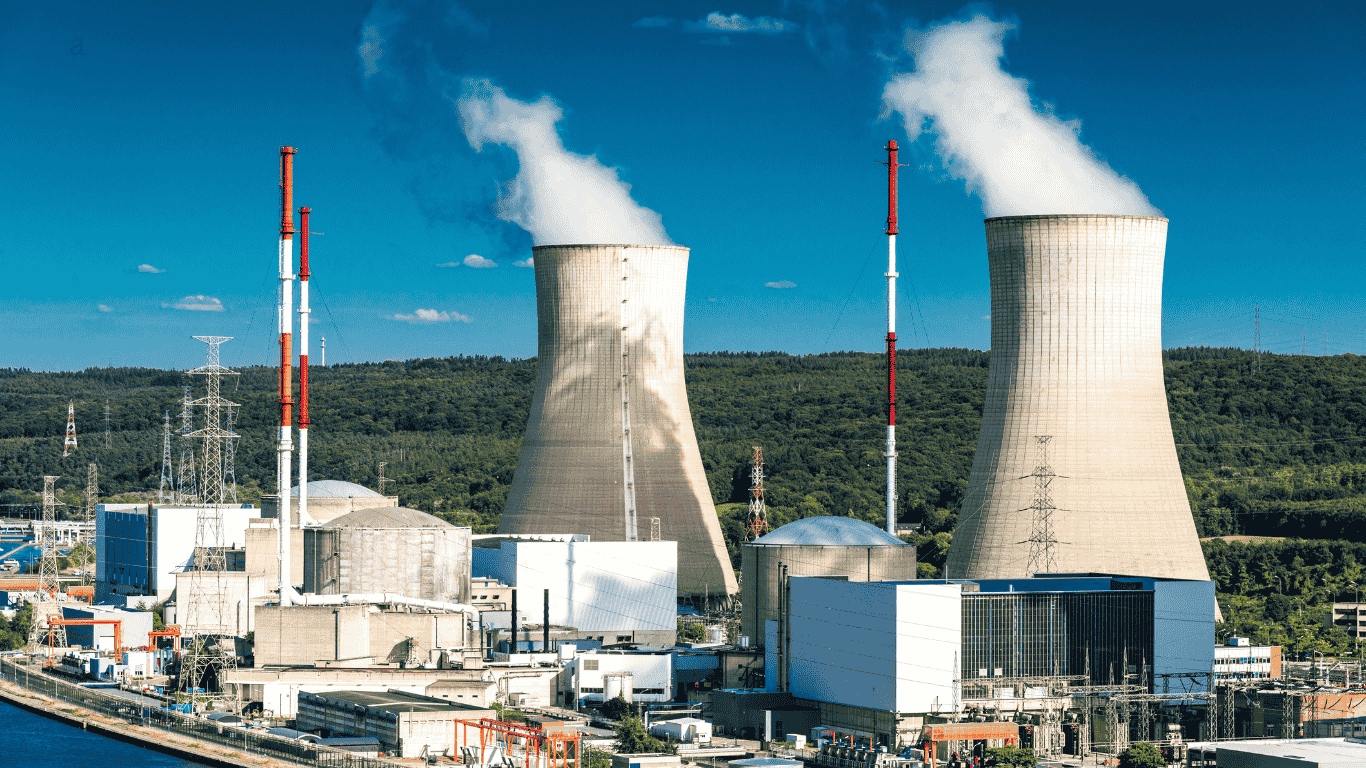
2. Nuclear Power Stations
Nuclear plants generate electricity using the heat produced from nuclear fission — the process of splitting atomic nuclei, typically uranium-235 or plutonium-239. This heat is used to create steam, which turns turbines and generates electricity. Nuclear energy provides a large amount of power with minimal carbon emissions, but it comes with concerns about radioactive waste and safety.
3. Hydroelectric Power Stations
These utilize the Power Supply of flowing or falling water — usually from a dammed river — to turn turbines. Hydropower is renewable, reliable, and emits no direct greenhouse gases.
4. Renewable Power Stations
These include solar farms and wind farms, which harness natural, inexhaustible resources.
- Solar power stations use photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors that concentrate sunlight to generate electricity.
As technology improves and environmental awareness grows, renewable they are playing an increasingly important role in the global energy mix.
5. Geothermal and Biomass Power Stations
- Biomass plants burn organic materials like wood chips or agricultural waste, offering a renewable yet sometimes controversial energy source.
Components of a Power Station
While the specifics vary depending on the type of power plant, most stations share several core components:
- Turbine: Converts fluid (steam, water, wind) movement into mechanical energy.
- Generator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Boiler or Reactor: Generates steam or heat, depending on the type.
- Control Systems: Regulate operations and ensure safety.
- Transformers and Transmission Lines: Step up voltage for efficient transmission and deliver electricity to the grid.
Importance of Power Stations
Power stations are essential to the functioning of society. Without them, critical services like hospitals, water treatment facilities, telecommunications, and transport systems would come to a halt. Economies would falter, and modern life as we know it would be impossible.
Moreover, it support innovation and economic development by providing the reliable electricity needed for businesses, schools, and homes. In developing regions, building power infrastructure is one of the first steps toward progress and improved living standards.
Environmental and Social Impact
While it provide massive benefits, they also come with challenges. Traditional fossil fuel plants contribute to air pollution and climate change. Nuclear stations raise concerns over radioactive waste and disaster risk. Even renewable energy projects can disrupt ecosystems and communities.
Today, much focus is on transitioning to cleaner, more sustainable power generation. Governments and private sectors are investing in renewable energy sources, smart grids, and energy storage to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
The Future of Power Generation
As the world moves toward cleaner energy, the future of it lies in innovation and integration. Emerging technologies such as energy storage systems, microgrids, and smart grids are changing how power is generated and distributed.
The ultimate goal is a resilient, sustainable energy system that provides reliable power without harming the planet.
Conclusion
Power stations are the engines of modern life. From their early beginnings during the Industrial Revolution to today’s cutting-edge renewable facilities, they have continuously evolved to meet the growing demand for electricity. As we face the twin challenges of energy security and climate change, the transformation of power generation will play a pivotal role in shaping our future.